|
The individual source images are not usually viewed separately, but combined into a single final set for diagnosis. These combined images are known by various names: diffusion-weighted images, isotropic images, or trace images. The most common method of image combination is to take the geometric mean:
|
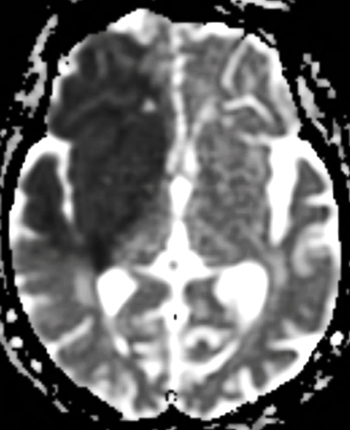
 Trace DWI of stroke
Trace DWI of stroke
The Trace DW image is not a map of diffusion; it is only diffusion-weighted, a fact implicit in its name. Trace DW images possess considerable T2-weighting. As such, lesions with either very long or very short T2 values may "contaminate" the Trace DW images, making them appear "artificially" bright or dark. These important phenomena are known as "T2-shine-through" and "T2-black-out", the subject of later Q&A's.
|
The ADC map is a pure display of consolidated ADC values. Because it is mathematically calculated it appears "pixel-ly" with "spots" scattered in the air around the subject. The signal intensities are opposite to those of the Trace-DW image, which can be a source of confusion. Tissues with short ADC values (like the stroke) appear dark, while materials like CSF with long ADC values appear bright.
|
Advanced Discussion (show/hide)»
Although 3-direction source DW imaging is still performed as described above, higher quality images can be obtained using more directions. We typically use at 6 directions for routine DWI, and 20 or more if performing diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). The trace of the diffusion tensor is computed from these multi-directional source images using a linear regression estimation technique that improves accuracy and signal-to-noise. The "trace" is rotationally invariant, meaning that it is the same regardless of which projections are used to measure it.
As described above, the ADC map is processed from the b0 and source DW images. On some scanners a "noise level" or similar thresholding parameter must be selected to determine which pixels are selected to produce the final map.
Minati L, Weglarz WP. Physical foundations, models, and methods of diffusion magnetic resonance imaging of the brain: a review. Concepts Magn Reson 2007; 30A:278-307.
Mukherjee P, Berman JI, Chung SW, et al. Diffusion tensor MR imaging and fiber tractography: theoretic underpinnings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2008; 29:632-640.
Schaefer PW, Grant PE, Gonzalez RG. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the brain. Radiology 2000; 217:331-345.
How do you make a DW image?
Which diseases are "bright" on DW imaging and why?
If a stroke is bright on a standard DW image, why is it dark on the ADC map?